Semantic segmentation and depth estimation lie at the heart of scene understanding and play crucial roles especially for autonomous driving. In particular, it is desirable for an intelligent self-driving agent to discern unexpected obstacles on the road ahead reliably in real-time. While existing semantic segmentation studies for small road hazard detection have incorporated fusion of multiple modalities, they require additional sensor inputs and are often limited by a heavyweight network for real-time processing. In this light, we propose an end-to-end Real-time Obstacle Detection via Simultaneous refinement, coined RODSNet, which jointly learns semantic segmentation and disparity maps from a stereo RGB pair and refines them simultaneously in a single module. RODSNet exploits two efficient single-task network architectures and a simple refinement module in a multi-task learning scheme to recognize unexpected small obstacles on the road. We validate our method by fusing Cityscapes and Lost and Found datasets and show that our method outperforms previous approaches on the obstacle detection task, even recognizing the unannotated obstacles at 14.5 FPS on our fused dataset (2048×1024 resolution) using RODSNet-2×. In addition, extensive ablation studies demonstrate that our simultaneous refinement effectively facilitates contextual learning between semantic and depth information.
Demo
We demonstrate the working demo of our network on real-world autonomous driving scenes.
Proposed Network
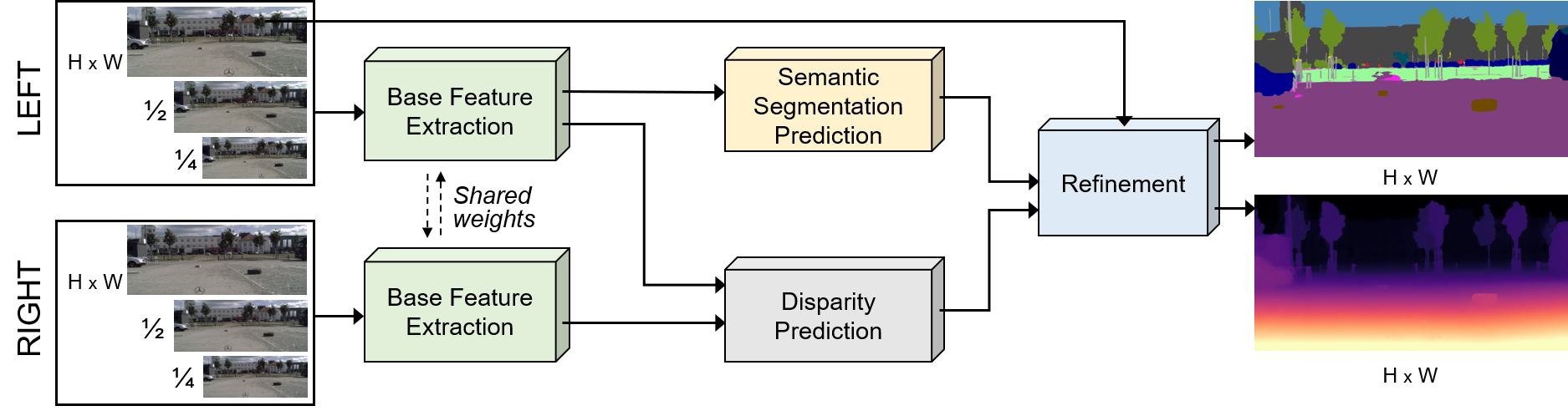
We propose an end-to-end network for Real-time Obstacle Detection via Simultaneous refinement, termed RODSNet. Given a pair of stereo RGB images, RODSNet jointly refines initial semantic and disparity maps in one stage, discerning both trained and unexpected roadside obstacles. Our network builds upon efficient single-task network architectures to estimate initial semantic segmentation and disparity maps, and adds a simple simultaneous refinement module to further improve both results. While we target real-time obstacle detection, this refinement module can also be coupled with other high-performing single-task networks at the expense of an increased computation time.
We highlight our main contributions in three-fold:
1. We propose a simple and efficient refinement module that simultaneously improves the predicted semantic segmentation and disparity maps. In contrast to other attention-based approaches, our module exploits a stacked hourglass network to promote contextual refinement with the initial semantic and disparity maps, and the left (reference) RGB image as inputs.
2. Our network outperforms existing semantic segmentation networks for road obstacle detection. RODSNet−2× achieves 2.6% and 1.7% improvements in segmentation accuracy for small obstacles (IoU) and all classes (mIoU), respectively, at 14.5 FPS inference speed on our fused dataset (2048×1024 resolution). Moreover, our ablation study demonstrates that it can be further tuned to better detect obstacles across all depth ranges than previous
methods.
3. The proposed network can be generalized to detect unannotated obstacles on the road. RODSNet effectively detects obstacles even in the absence of proper annotations by leveraging both semantic and geometric contexts from our multi-task learning architecture.
Network Modules
Our multi-task learning network consists of the following modules: Base feature extractor, initial semantic segmentation and disparity map estimation, and simultaneous refinement.
Base feature extractor
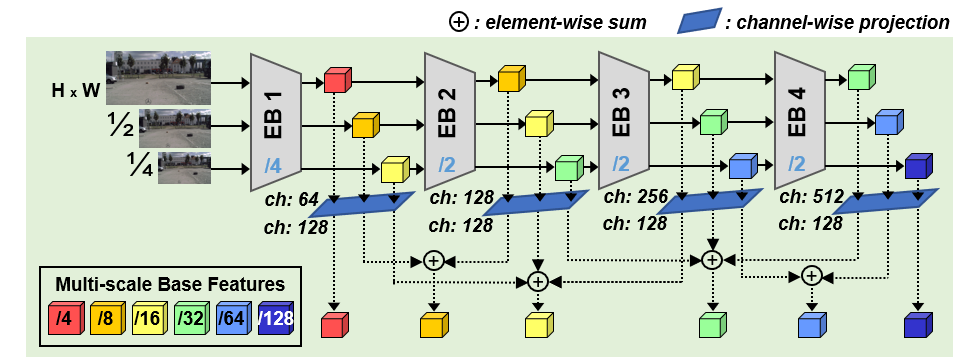
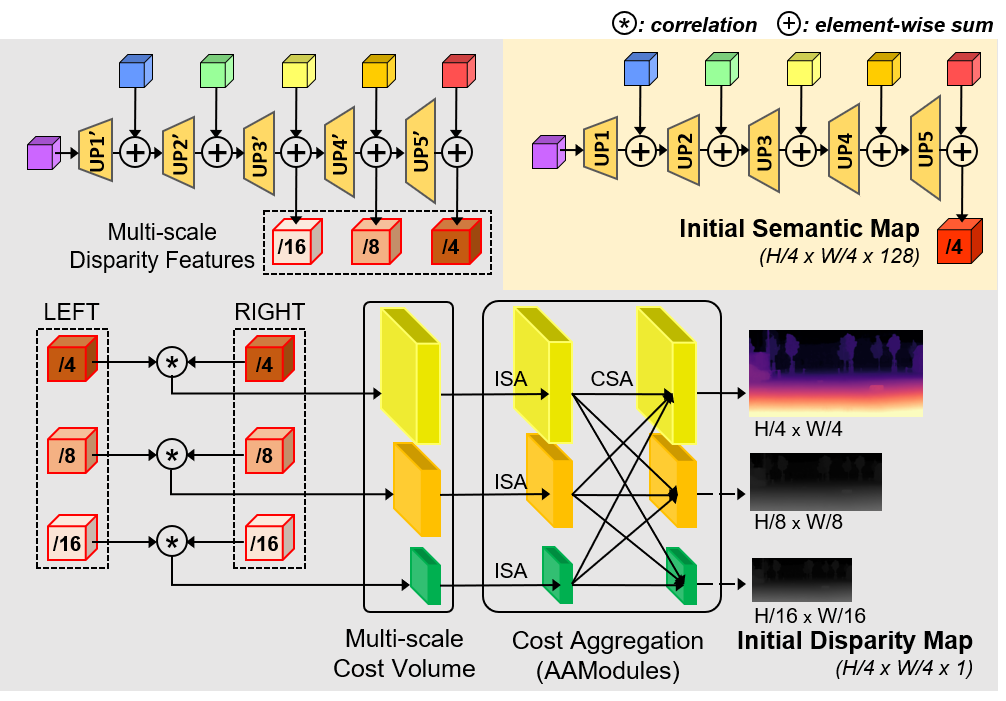
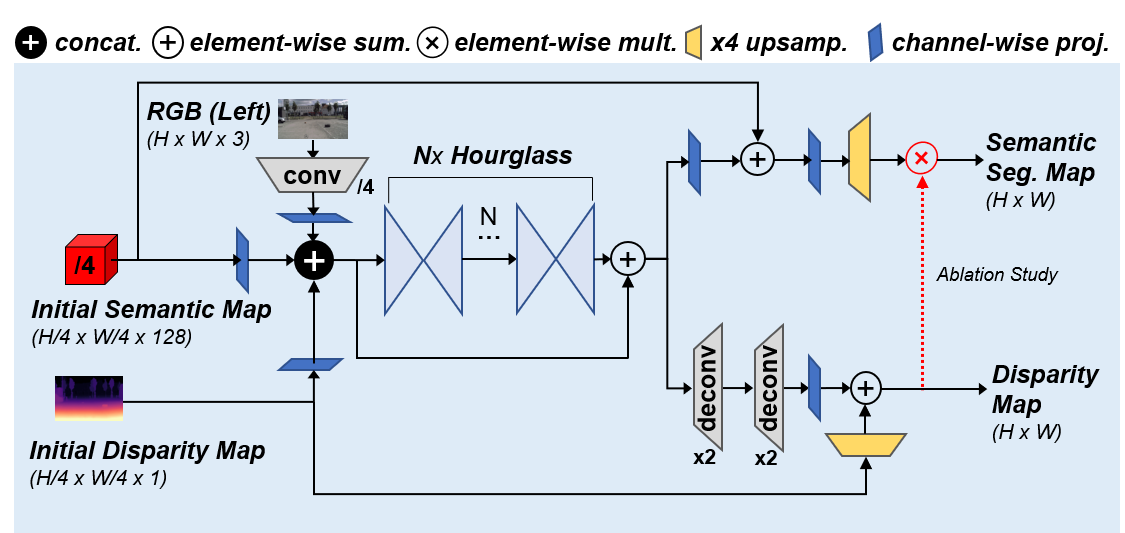
Citation
@article{songjeong2021rodsnet,
author = {Song, Taek-jin and Jeong, Jongoh and Kim, Jong-Hwan},
title = {End-to-end Real-time Obstacle Detection Network for Safe Self-driving via Multi-task Learning},
year = {2022},
doi = {10.1109/TITS.2022.3149789},
URL = {https://doi.org/10.1109/TITS.2022.3149789},
journal = {IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems (T-ITS)}
}
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Institute for Information & Communications Technology Promotion (IITP) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIT) (No.2020-0-00440, Development of Artificial Intelligence Technology that Continuously Improves Itself as the Situation Changes in the Real World).